Air plasma cutters
Portable, powerful and incredibly versatile, air plasma cutters are made for cutting, gouging, and marking metal in light metal applications, using a hand or mechanized torch such as on a CNC plasma cutting machine. For metal workers who need to easily and reliably gouge and cut metal up to 38 mm (1-1/2″). See our product line.
Conventional single flow plasma
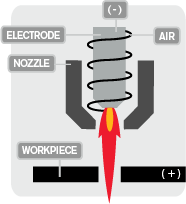 A conventional single flow process is when the compressed gas flows in between the electrode and nozzle. The negatively charged terminal (electrode) initiates the plasma arc between the nozzle, then the pilot arc, during transfers with the positively charged terminal (workpiece). The electric arc charges the gas and excites the electrons, turning it into ionized gas, otherwise known as plasma gas. In this state, the ionized gas becomes plasma (fourth state of matter) and is used to cut metal. The gas also helps cool the torch itself and helps blow high temperature molten metal away from the cut, reducing dross and slag. Commonly, compressed air is used, and its utilization is cost-effective and versatile, generally used in handheld plasma cutting systems such as the Powermax line of plasma cutters from a 30-amperage plasma cutter to up to our 125-amperage plasma cutter. The Powermax30 AIR plasma cutter has great versatility and comes with an internal air compressor for convenience.
A conventional single flow process is when the compressed gas flows in between the electrode and nozzle. The negatively charged terminal (electrode) initiates the plasma arc between the nozzle, then the pilot arc, during transfers with the positively charged terminal (workpiece). The electric arc charges the gas and excites the electrons, turning it into ionized gas, otherwise known as plasma gas. In this state, the ionized gas becomes plasma (fourth state of matter) and is used to cut metal. The gas also helps cool the torch itself and helps blow high temperature molten metal away from the cut, reducing dross and slag. Commonly, compressed air is used, and its utilization is cost-effective and versatile, generally used in handheld plasma cutting systems such as the Powermax line of plasma cutters from a 30-amperage plasma cutter to up to our 125-amperage plasma cutter. The Powermax30 AIR plasma cutter has great versatility and comes with an internal air compressor for convenience.
Dual flow plasma
The base of the process is very similar to the single flow plasma. It uses plasma gas, but it has a secondary gas flow which gets pushed in between
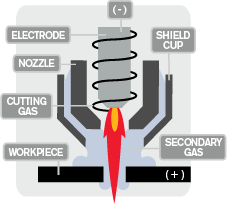
the nozzle and the shield and enhances performance. The secondary gas flow is called the shield gas. While air can be used as the shield gas, other types of gas that gets used are Nitrogen (best for stainless steel), Argon-Hydrogen Mix (best for thicker materials or high-alloy metals). The performance benefits from the secondary gas are cleaner cuts (less dross), increased cutting speed, extended torch life (better cooling). The secondary gas flow also helps shield the cut from oxidation.
High definition class plasma
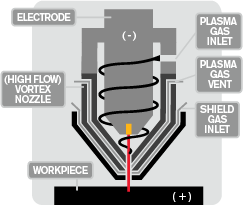
Sometimes called high-precision plasma, this plasma type offers exceptional cut quality with fast cut speeds and low operating costs in high volume, heavy production environments.
In this process, a specialized nozzle design narrows the arc and increases energy density. Because of the higher arc energy, high-definition plasma cutters achieve superior cut quality on conductive materials up to 50 mm (2”) with superior cut edge angularity, narrower kerf, and higher cut speeds than conventional plasma cutting technology. It's not uncommon with these systems to achieve cut part accuracies within tolerances of +/- 0.25 mm (0.010") range.
Today’s high-definition plasma cutters allow very high levels of automation and are intended for automated applications only. In the most advanced systems, virtually all of the CNC machine operator’s expertise (required to get good cut quality on earlier plasma systems) is essentially captured in the CAM software that manages the day-to-day machining cutting operations.
With a high-definition plasma cutter, it is possible to cut holes that are round and have virtually no taper- when using technology such as TrueHole (part of the Hypertherm SureCut suite) and have matching capability of table motion and THC control. Edges are square and can be dross free with refinement. Cut-to-cut cycle times allow much higher levels of productivity than with traditional types of plasma. A single plasma system can cut material thicknesses from thin gauge like sheet metal to over 182 mm (6”), using the same plasma torch. The plasma torch can cut and mark the plate through the same nozzle orifice. The cutting process is faster than oxy fuel cutting and laser cutting in thicker metal and beveling applications.
X-Definition class plasma
The industry’s newest and most advanced plasma cutting technology, X Definition ® plasma, sets a new standard for cut quality and consistency on mild steel/low carbon steel. It also expands the application of Hypertherm’s pioneering high-definition process to a broad range of non-ferrous applications.
When installed on a high-quality automated cutting machine, X-Definition plasma can deliver precision edge angularity that rivals laser — up to ISO 9013 Range 2 on thinner materials and Range 3 on thicker conductive metals, with greater consistency.
With high definition plasma cutters, including HPR above, other gases beyond air can be used such as nitrogen (best for stainless steel and aluminum), argon (best with non-ferrous metals), hydrogen (often mixed with argon for cutting thick stainless steel or aluminum), and oxygen (best for cutting mild steel/low carbon steel).
X-Definition is more than a single design innovation. It consists of a number of expanded cutting technologies/cutting methods.
Additional expanded cutting technology within X-definition
HyFlow vortex or vented nozzle technology
A unique two-piece vented nozzle design that aligns and focuses the plasma arc for increased arc stability and energy density, resulting in a cleaner, sharper, more consistent edge quality on all steel (including stainless) and aluminum.
Vented Water Injection (VWI)
Patent pending process featuring a vented N2 plasma gas and H 2 O shield gas for less angularity and squarer cut edges on aluminum as well as stainless steel.
Vent-to-shield
Technology in which hydrogen from the vented plasma gas is reclaimed and mixed with the shield gas, reducing angularity and delivering more consistent edge color on stainless steel up to 12 mm (15/32 inches).
Plasma dampening
Patent pending technology that adds a chamber in the nozzle to absorb the pressure and flow fluctuations that create arc instability during cutting with lower current, highly constricted arcs required for thin stainless applications. This eliminates wavy and irregular cut surfaces.
Cool nozzle™
Patent pending feature on the 300-amp oxygen process in which liquid cooling is sent directly to the nozzle bore, increasing cut quality over the life of the consumables by more than 40%.
Advanced arc stability
Technology that modifies impingement of the shield gas for improved arc stability when coming out of a pierce hole or out of an acute angle for reduced lead-in lengths, precise cuts, and improved quality cuts.
See our X-Definition product line.
