Types of applications
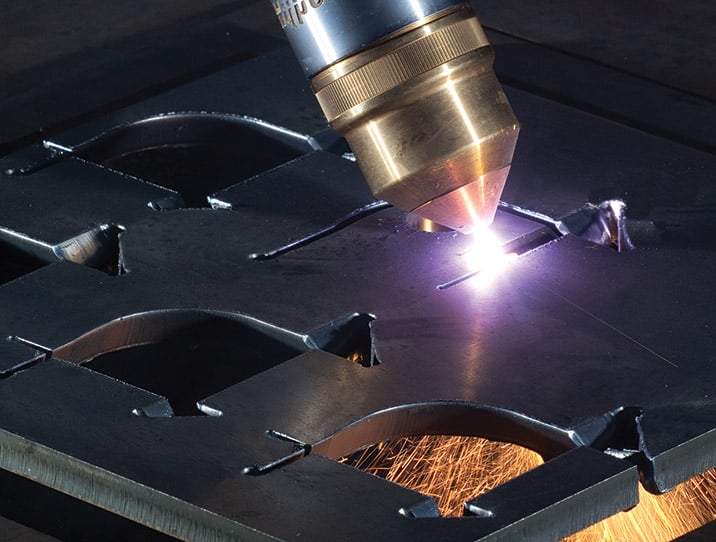
Plasma arc cutting is used in both handheld and mechanized systems to cut a wide range of conductive materials, including mild steel, carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper, brass, and other metals. With a variety of systems, accessories, and consumables available, plasma cutting is one of the most versatile and easy-to-use cutting technologies available for all kinds of metalworking and fabricating applications.
Cutting solutions
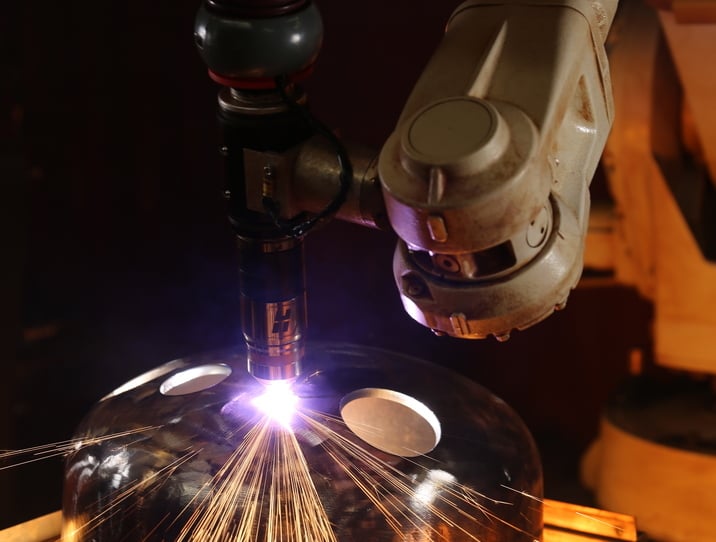
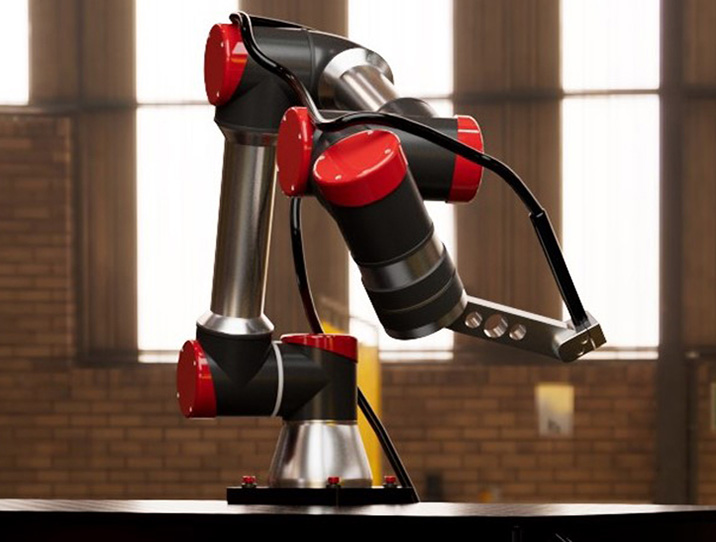
Robotic plasma cutting
Robotic cutting systems support your most complex projects. Combined with robot programming, robotic plasma cutting dramatically improves efficiency by increasing cut speeds, cut quality, and production in low-volume runs — returning hundreds of hours to your business.
Cobot plasma cutting
Metal fabricators who want to increase productivity and product throughput choose cobot plasma cutting. This innovative solution provides rapid, consistent, and safe cutting and gouging outcomes while reducing secondary operations—all without a significant investment or lengthy learning curve.
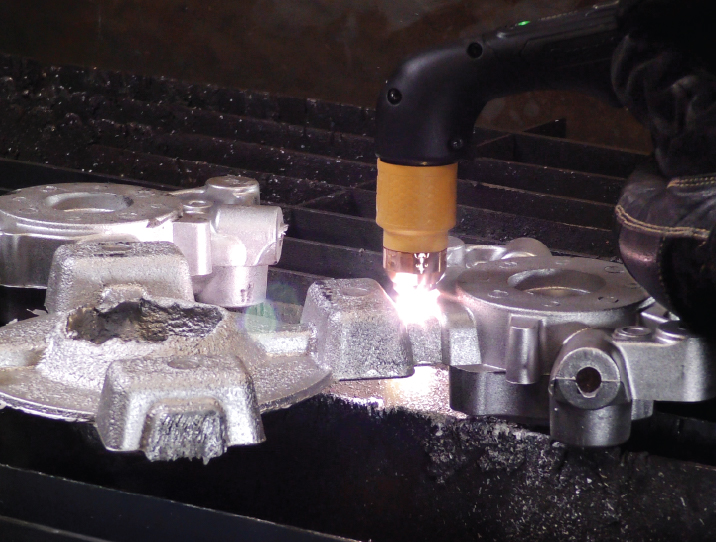

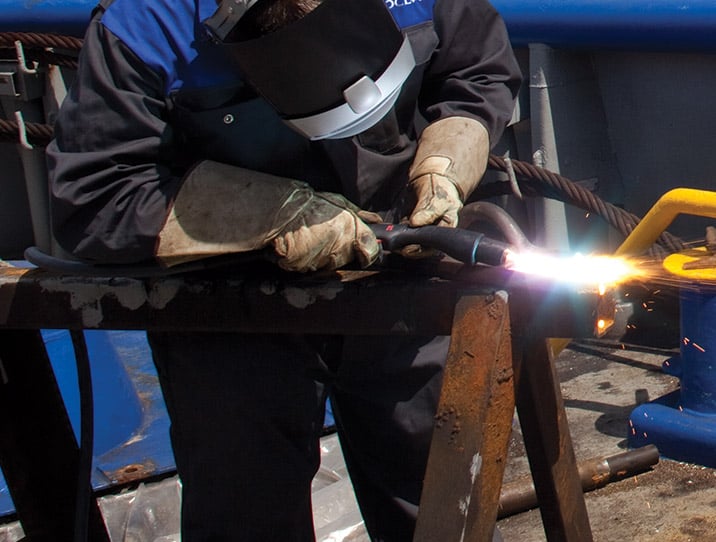
Cast trimming with plasma
Foundries and automotive manufacturers degate and trim castings more effectively with plasma than with other labor-intensive and less efficient methods. Trim castings safer and quicker with proven handheld and automated plasma cutting solutions.
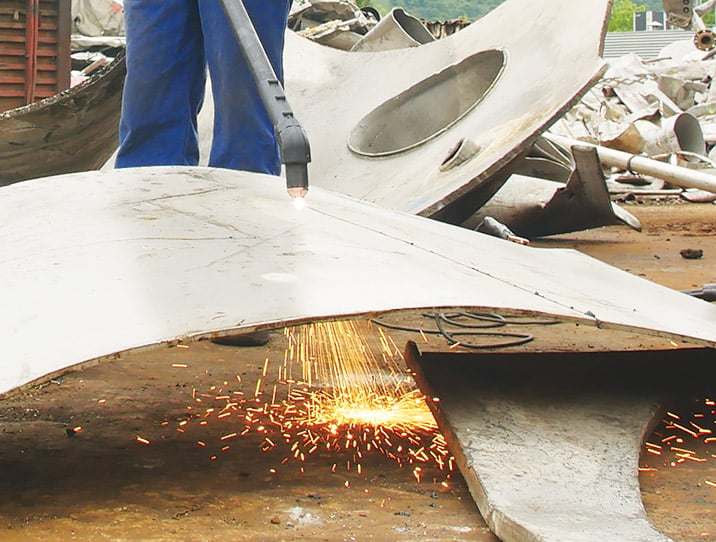
Scrap cutting
Plasma cutting can be instrumental in salvaging various thicknesses of scrap metal from old appliances, industrial equipment, cars, and other items as an important part of the lifecycle of raw materials. It minimizes waste, maximizes the value of manufactured goods, and significantly reduces environmental impact.
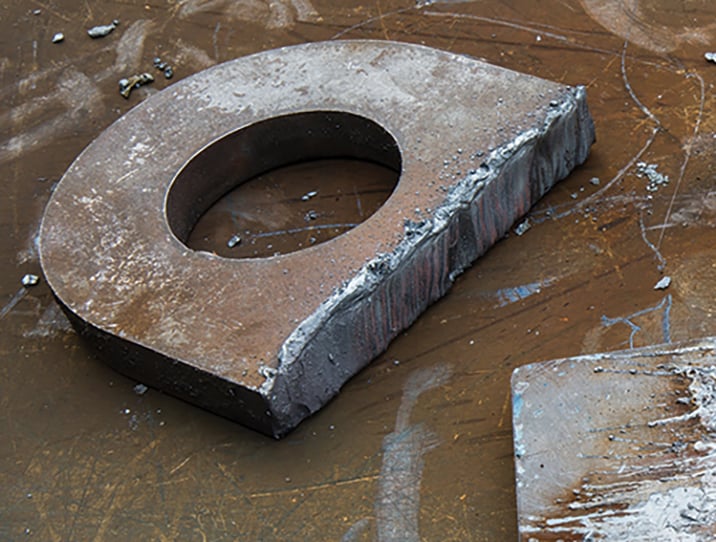
Plasma bevel cutting
Bevel cutting is cutting a part with an edge not perpendicular to the top of the piece. It is typically used to prepare plates or pipes for welding. Bevels can be cut at different angles and configurations, resulting in varying edge profiles.
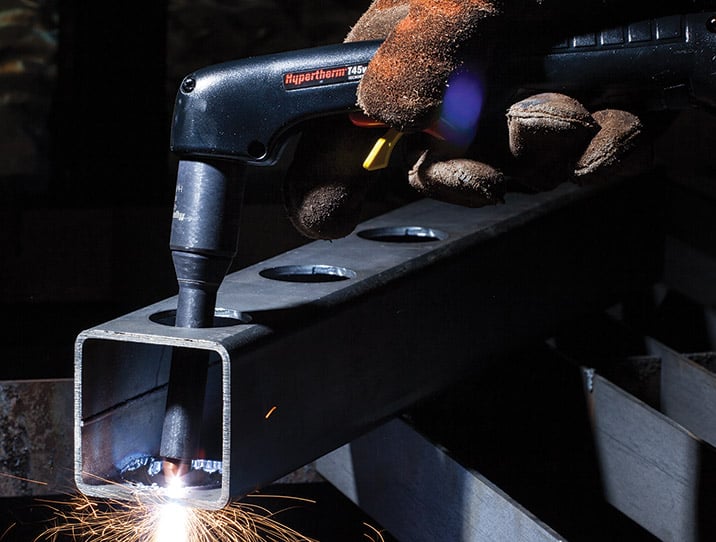
Extended reach cutting
Hypertherm’s HyAccess® extended reach consumables give users extra reach when plasma cutting or gouging in hard to access or confined spaces, and are designed for use with Powermax air plasma systems.
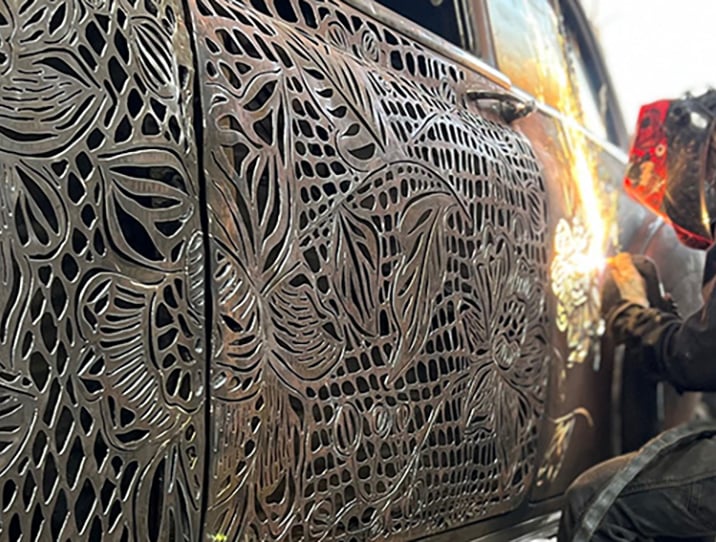
Fine feature cutting
When cutting parts with very fine details or intricate shapes, you need processes capable of producing very thin kerfs.
Plasma flush cutting
FlushCut® consumables for Powermax® systems allow easy removal of protrusions, welded attachments, bolts, and fixtures from metal surfaces without cutting into the base material.
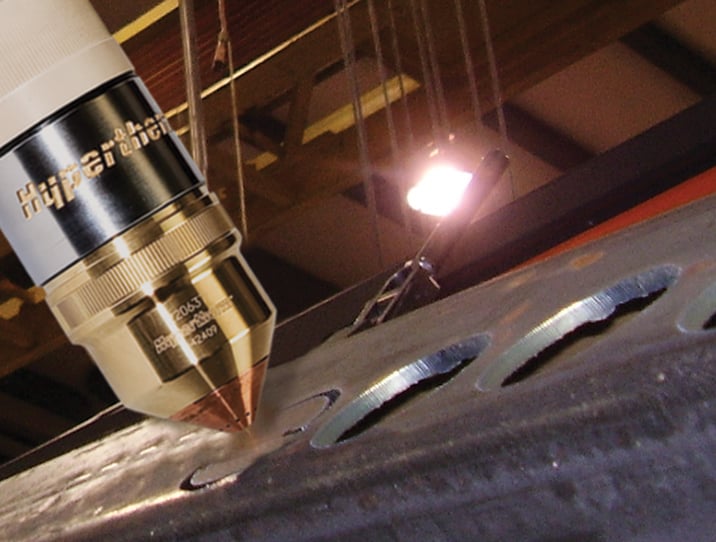
Plasma hole cutting
Many fabrication processes require cutting holes to bolt two or more pieces or parts together, so hole production is an important part of most cutting operations. Multiple holes can be cut into a large plate, pipe, or drum with plasma.
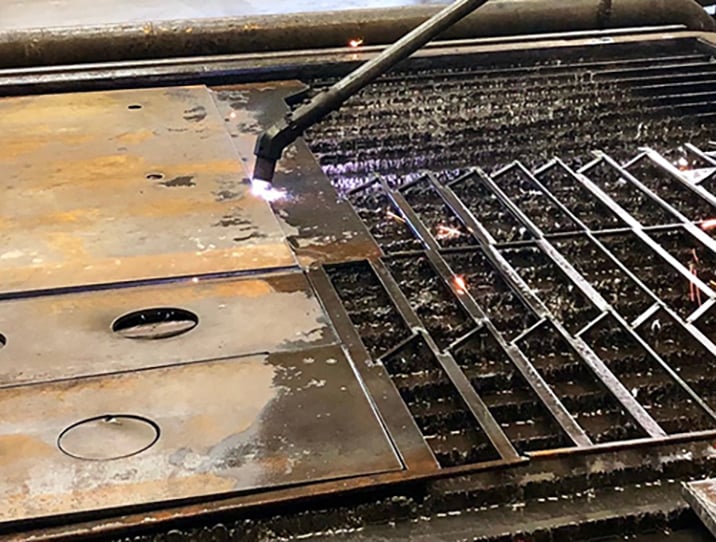
Skeleton cutting
Cutting up and removing the remnants of a metal plate ("skeleton") after mechanized cutting is typically slow and labor-intensive, with many safety risks. Skeleton cutting with plasma is faster, safer, and can be easily integrated into automated cutting operations.
Gouging & metal removal
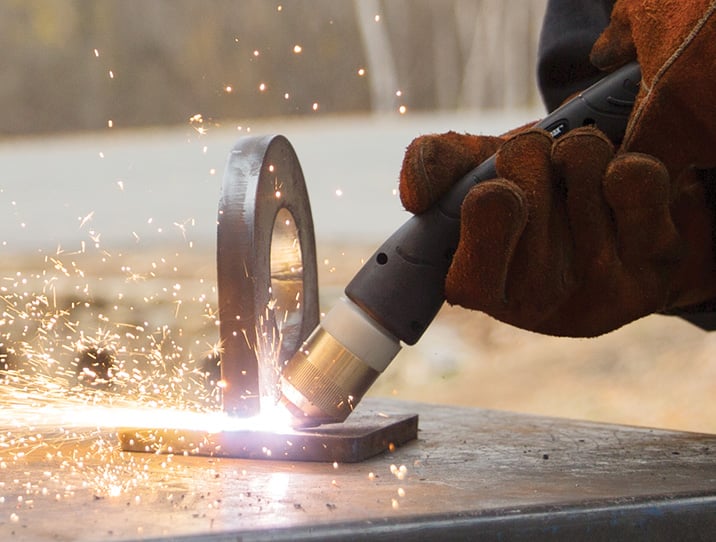
Plasma gouging
Plasma gouging – removing metal using a plasma arc – is similar to plasma cutting. A plasma arc between the torch and the workpiece melts the metal, and a gas jet blows away the molten material.
Temporary attachment removal
Flush cutting with Powermax® plasma systems lets you cut closer to base materials than ever before, reducing costly, time consuming secondary operations. Cleaner cuts with less damage to the base metal saves costs in reusable temporary attachments.
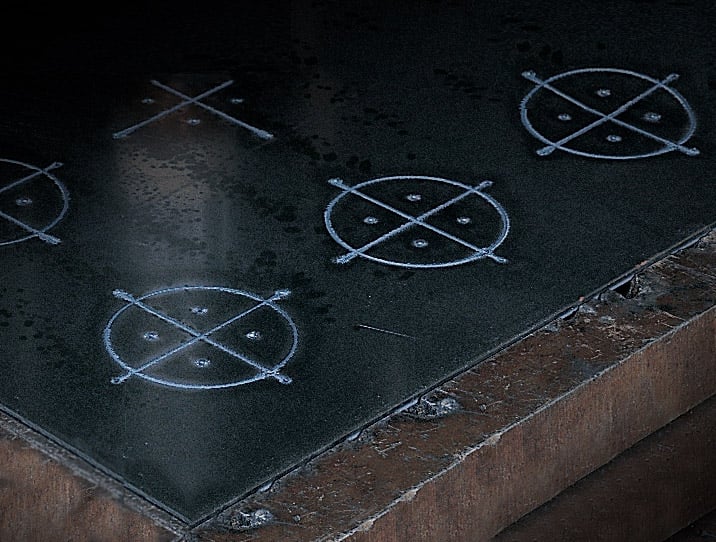
Marking
Plasma marking
Marking metal to indicate bend or score lines, inventory numbers, or reference points for drilling or robotic processes is traditionally done with a hammer and punch, powder or ink, soapstone, or handheld engraving machines. Using plasma for marking during CNC processes offers many significant advantages.
Fabrication & automation
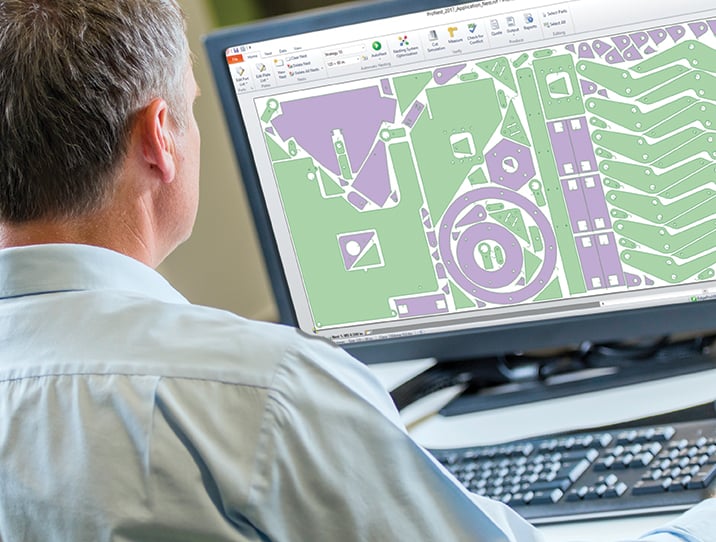
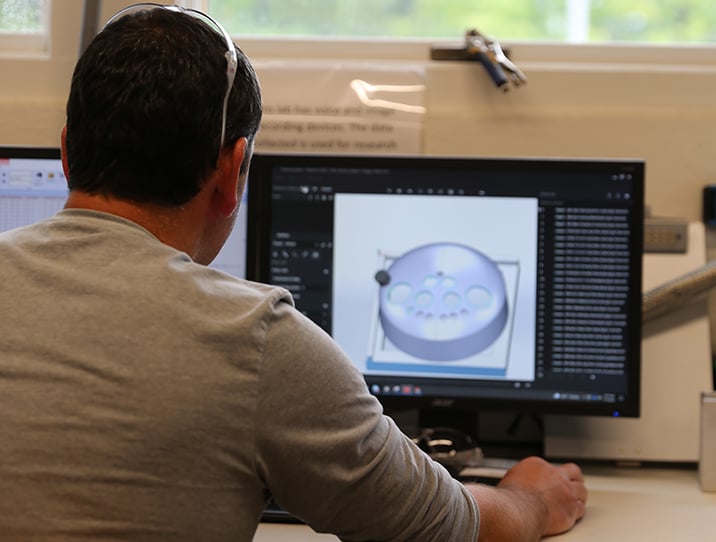
CAM programming
CAM software helps drive the manufacturing process. CAD/CAM nesting software is typically used for programming mechanized flat plate cutting, offering fabricators and manufacturers a single software solution for all of their profile cutting needs. This combination solution provides all of the necessary functionality to complete the job, from CAD concept, to part preparation, to nesting, to numeric code output.
CNC programming
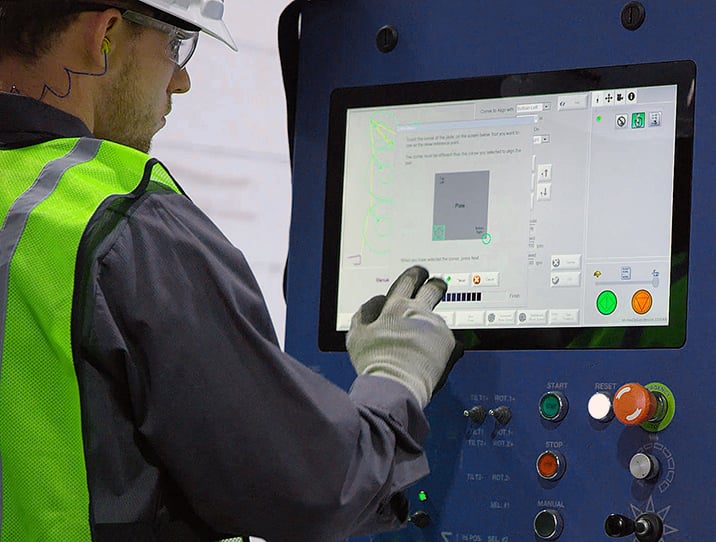
With built in cutting expertise, Hypertherm’s Computer Numeric Control solutions provide consistent product performance with our easy to learn and use Phoenix® software so operators make the optimal cut, every time.
Robot programming
Offline programming solutions to maximize robot productivity on high-mix, low-volume production runs. Reduce programming time, easily program parts of varying complexities, and eliminate the robot downtime associated with manual or teach pendant programming.















