Automated cutting systems: a guide

Automated cutting—whether plasma, laser, waterjet, punch, or something else - encompasses many different cutting processes in which the cutting tool is moved using mechanical means. This can include cutting on a XY table, or the use of other mechanical means such as pipe cutters or robots. These different production processes can reduce downtime, improve workflows, and enhance a production line.

X-Y-Z cutting and gouging
X-Y-Z cutting and gouging, often called XY cutting, is the use of a table equipped with a computer numeric control (CNC) for rapid and precise cutting of flat plate. The CNC moves the torch along the X and Y axes, while a height control system regulates the Z, or up and down motion, keeping the torch or cutting head at an optimum distance from the plate.
Though people often think of a CNC plasma, sometimes called a computer plasma cutter, you do not necessarily need to use plasma. Laser, waterjet, and oxyfuel are also suitable processes.
Whether you choose to use a plasma CNC machine or not, these tables are available in a wide range of sizes and prices.
-
The smallest use a standard personal computer as the CNC (CNC plasma cutting machine, laser, waterjet, or oxyfuel) and can be as small as 2′ by 2′. How to choose a small CNC plasma cutting table.
-
High-performance industrial CNC plasma cutting tables (or waterjet, laser, and oxyfuel) can be as long as 100′ and often have multiple torches mounted on one or more gantries for mass production and fabrication.
Typical uses include:
-
Plate cutting
-
Precision cutting of metal, stone, or foam
-
Cutting of parts in large quantities
Process technologies used:

Straight track cutting and gouging
Track cutting and gouging is used to make long, straight cuts or gouges that are difficult and time-consuming to do by hand with the necessary precision. Straight rack cutting is sometimes used on a job site when the material to be cut or gouged is of a size or shape not suited to an X-Y table. Automating these processes with a portable track burner increases productivity and results in a more uniform cut or gouge. Although originally designed for use with oxyfuel torches only, many suppliers now produce straight track burners capable of delivering the high speeds needed when cutting with plasma.
Typical uses include:
-
Shipbuilding
-
Pressure vessel fabrication
-
Scrapping I-beams
-
Structural steel applications
-
Back gouging welded plates
Process technologies used:
-
Plasma cutting
-
Plasma gouging
-
Oxyfuel cutting
-
Carbon arc gouging

Pipe and tube cutting
Rotary pipe and tube cutting capability is now commonly available via both stand-alone machines and as part of an add-on option for X-Y cutting tables. These machines offer the ability to mount pipe and tube sections and cut profiles from the pipe or tube wall. Extremely accurate profiles can be cut using exterior dimensions, wall thickness, rotational motion, and other required factors, ensuring ease of fit-up prior to welding, or simply for aesthetic or architectural purposes. Advanced programming even makes it possible to include bevel angles to assist with weld preparation.
Pipe cutting software
Hypertherm’s Rotary Tube Pro™ pipe cutting software is designed for today’s mechanized pipe cutting applications and makes it easy to design and cut tube and pipe parts.
Typical uses include:
-
Oil and gas pipelines and platforms
-
Ship and boat fluid and steam transfer
-
Industrial machinery structures
-
Construction industry structures
Process technologies used:
-
Plasma cutting
-
Laser cutting
-
Waterjet cutting
-
Oxyfuel cutting
Beam processing
Traditionally, beam fabrication has involved multiple processing machines, each performing a different function. Today, beam processing machines – most of which involve robotic or articulating arm designs – perform multiple applications such as coping, bevels, slots, holes, notches, and marking, all on the same heavy-duty machine. This not only saves time, but also increases part accuracy, improves cut quality, and is more cost-effective. The machines are used by the structural steel industry to build frame materials and in the building of power and chemical plants, refineries, trailers, rack systems, and bridges.
Typical uses include:
-
Fabrication of large beams including the cutting of beveled edges
-
Cutting of slots, holes, copes, notches
-
Marking of beams
Process technologies used:
-
Plasma cutting
-
Oxyfuel cutting
-
Laser cutting
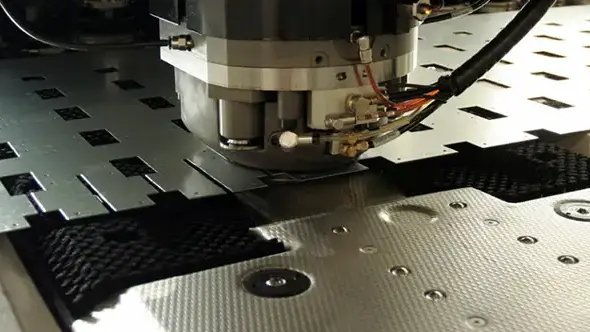
Punch processing
Punch processing of flat sheet or plate is commonly performed using one of two machine formats. First, stand-alone punch machines, known as turret punches, offer automated operations including punching, contour cutting (nibbling), and tapping. Because of their versatility, turret punch machines are highly effective as punch processing tools. The process delivers highly accurate holes, without exposing workpieces to damage from heat-affected zones.
A second machine format integrates punch capability into an X-Y plasma cutting system, laser, or plate processing machine. By bringing these processes together, fabricators can enjoy superior productivity thanks to reduced material handling time and improved part quality. In addition, these integrated machines save on floor space.
Combination plasma/punch and combination laser/punch typically feature a traditional cutting table with the added ability to reposition the workpiece to a dedicated punching station. (These machines are sometimes referred to as reposition machines.)
Plate processing machines combine cutting, punching, drilling, and other tools in one highly versatile machine.
Typical uses include:
-
Structural components and cases for electronics
-
Small appliance hardware
-
Structural bolt-hole applications
Process technologies used:
-
Punching
-
Tapping

Robotic cutting
Robotic cutting is an automation solution that is continuing to build in popularity. Many industries use robots in varying configurations, or “work cells,” to perform tasks that may be completed more efficiently and profitably than manual labor. In the past, robots were limited to those with very high production quantities, because teaching the robot was a lengthy and expensive process, often taking weeks to complete for a single part/job. However, recent robotic software programming developments, such as Hypertherm’s Robotmaster® offline programming software for robots, have taken robotic cutting to the next level by reducing programming time – what used to take weeks can now be done in minutes. As a result, robots are more commonly being used for low-volume manufacturing processes and high-mix applications.
Typical uses include:
-
Cutting for applications such as domes and I-beams
-
Welding in automotive and other industrial applications
-
Machining operations
-
Painting/spray coating / thermal protection coating of molds
-
Polishing, sanding, and grinding using a variety of tools and techniques including belt sanders, abrasive discs, wheels, laps, brushes, and pads
-
Deflashing of plastic molded parts
-
Dispensing of seals and adhesives
Process technologies used:
-
Plasma cutting
-
Laser cutting
-
Waterjet cutting
-
Routing
-
Sanding
-
Spraying
-
Taping
Hypertherm: the high-quality power supply for any automated cutting system
Hypertherm is the industry-leading cutting technology whether you are using cutting-edge robotics, an X-Y table, or other cutting solutions. There are lots of options when it comes to automated cutting equipment- make sure your cutting operations are powered by a world-class Hypertherm plasma cutter and genuine Hypertherm consumables.




